Google Drive’s new AI-powered ransomware detection shields user files from corruption and enables rapid recovery. Image Source: ChatGPT-5
Google Adds AI-Powered Ransomware Protection to Drive for Desktop
Key Takeaways: AI Defense Against Ransomware in Google Drive
Google has announced AI-powered ransomware detection in Google Drive for desktop, available on Windows and macOS.
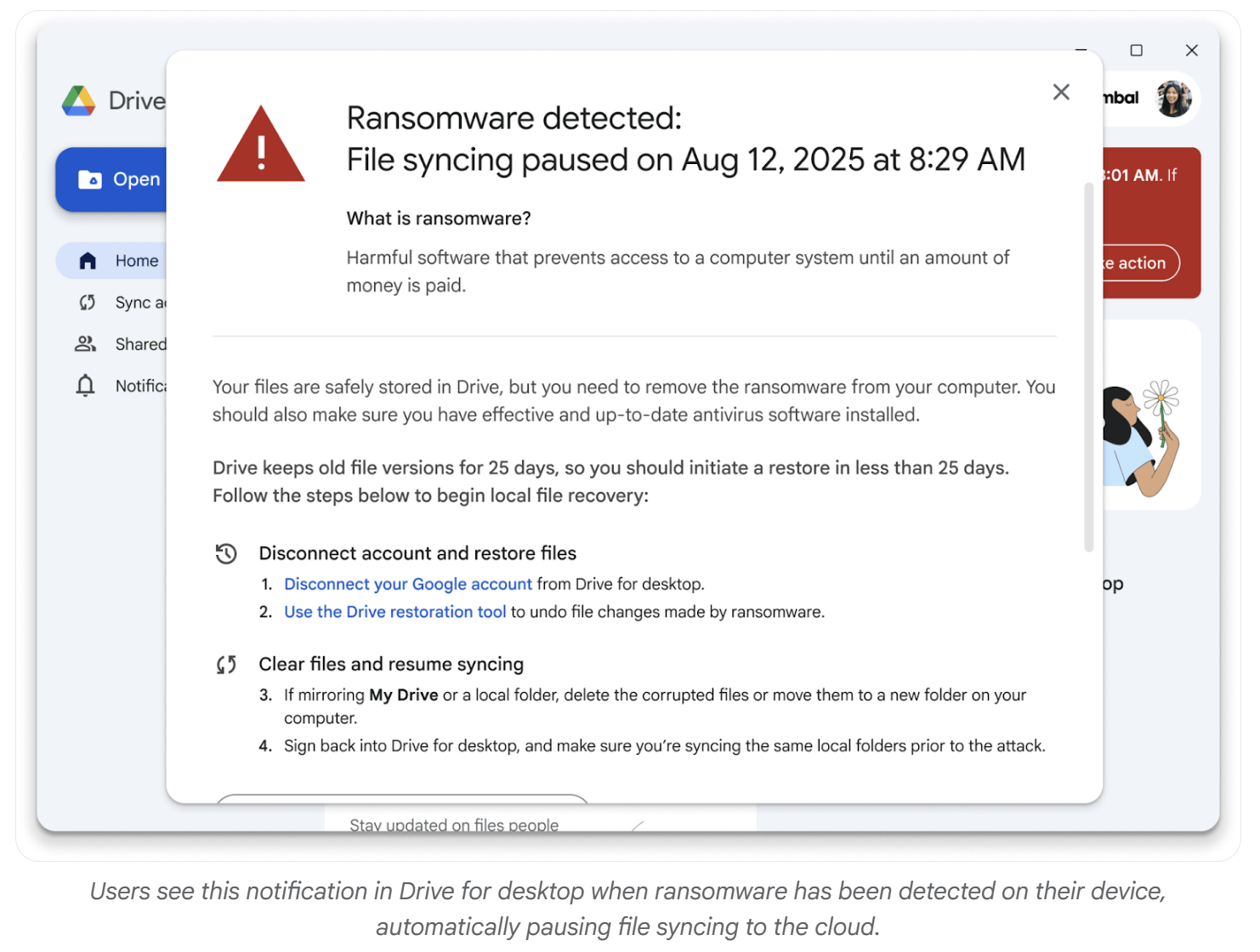
The system halts file syncing when ransomware activity is detected, preventing widespread corruption.
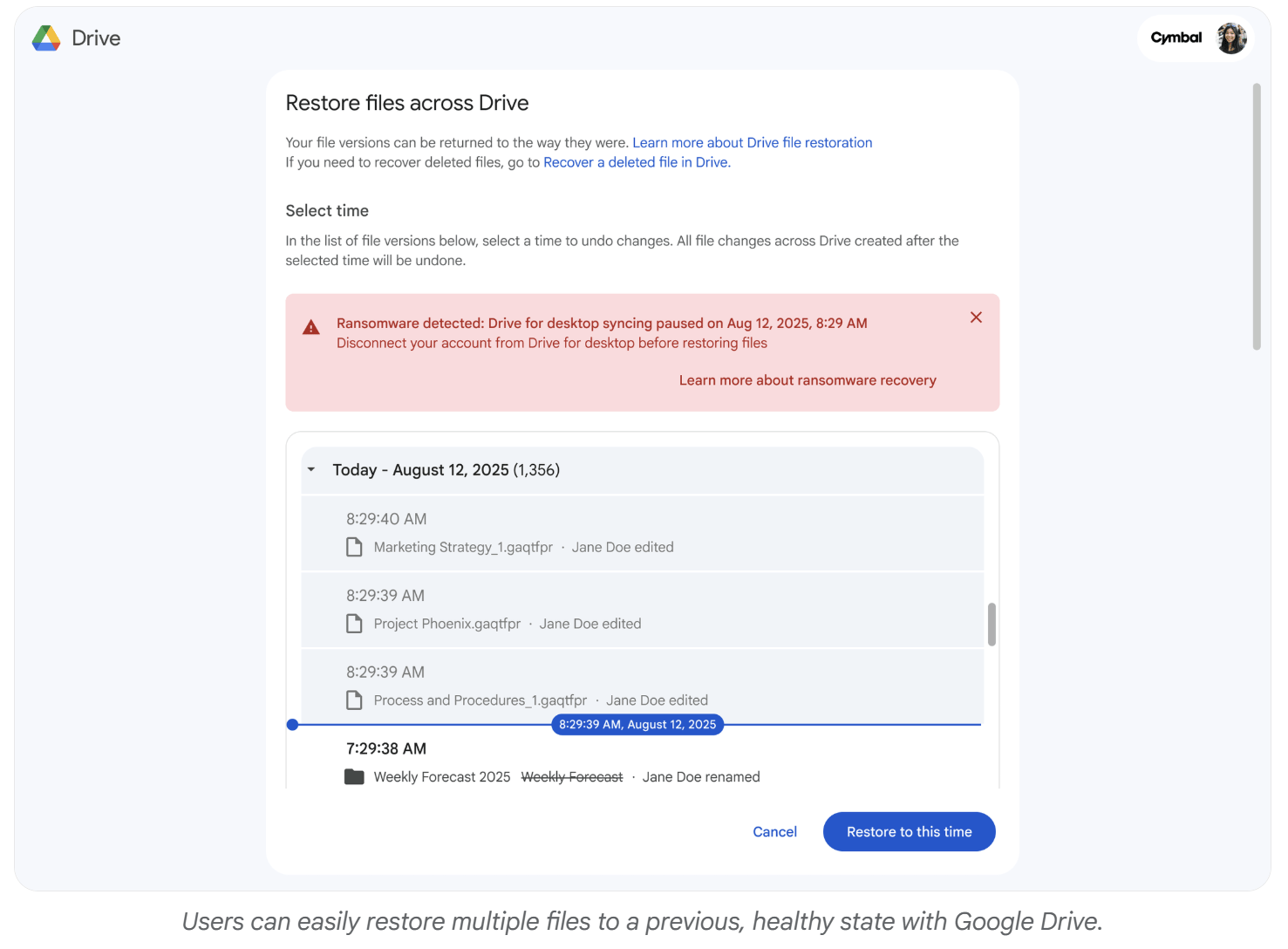
Users can restore files to a previous healthy state with just a few clicks, reducing downtime and data loss.
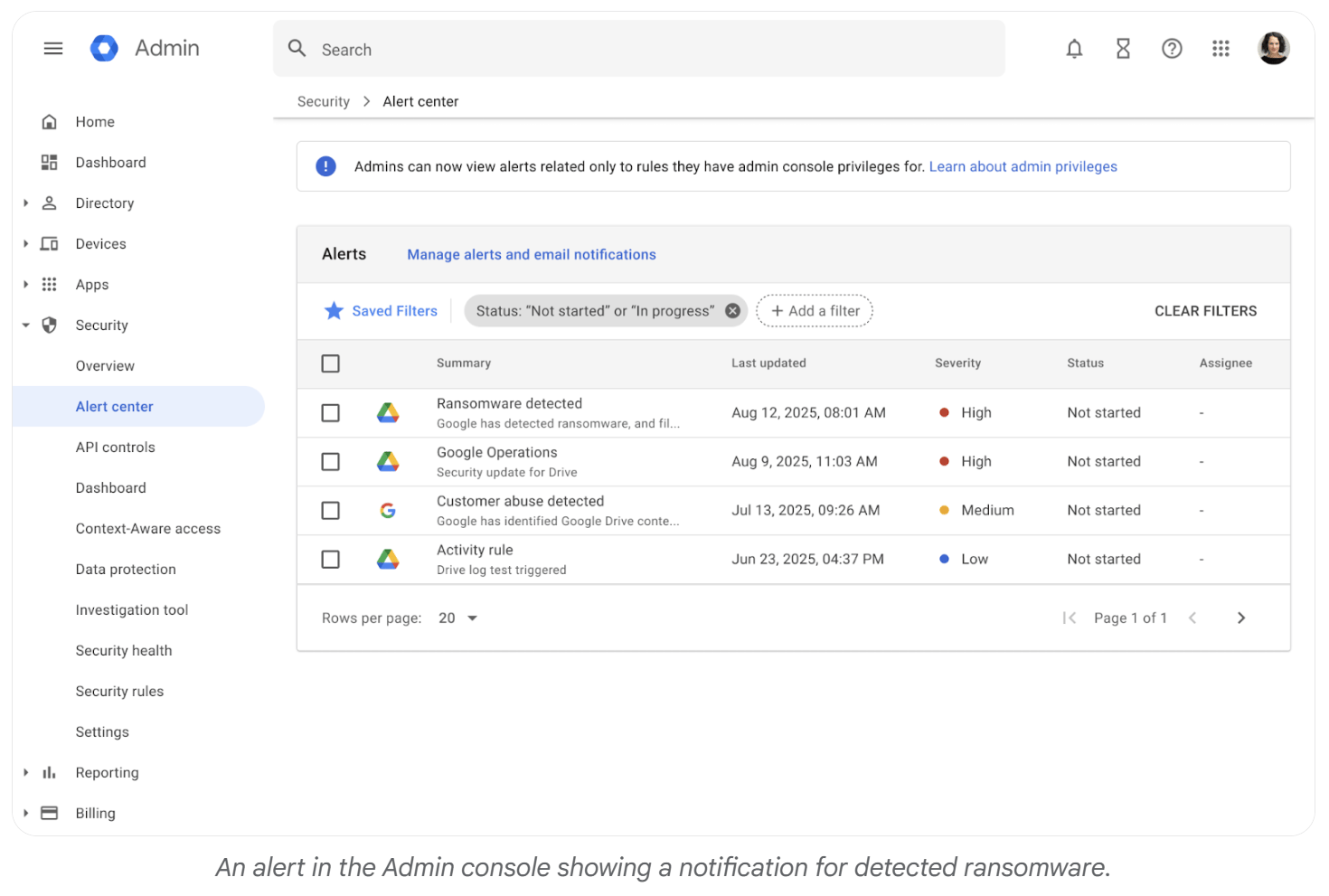
Admins receive detailed alerts and controls via the Google Workspace Admin Console.
The feature is rolling out today in open beta, included at no additional cost for most Workspace commercial plans and consumer users.
Google Drive Introduces AI-Powered Ransomware Detection
Google has announced new AI-driven ransomware protections for Google Drive for desktop, designed to stop attacks before they spread and to simplify file recovery. The update applies to Windows and macOS devices, with rollout beginning today in open beta.
Ransomware remains one of the most damaging cyber threats facing organizations today. In these attacks, malicious software encrypts or locks critical files and then demands payment for their release. The result can be severe financial losses, extended downtime, and compromised data — disruptions that affect organizations of every size and across industries such as healthcare, retail, education, manufacturing, and government.
The move comes as ransomware continues to grow as a cybersecurity threat. According to Mandiant, ransomware accounted for 21% of observed intrusions last year, with the average incident costing organizations more than $5 million.
“By seamlessly integrating AI-powered ransomware detection and restore capabilities into Drive, Google is helping organizations with an innovative way to avoid an increasingly common and increasingly dangerous threat,” said Bob O'Donnell, President and Chief Analyst at TECHnalysis Research.
Why Ransomware Protection Matters
Ransomware attacks target critical sectors such as healthcare, retail, education, manufacturing, and government, where downtime can disrupt essential services.
While native Google Workspace documents such as Docs and Sheets are not vulnerable to ransomware, and ChromeOS has never experienced a ransomware attack, other common file types like PDFs and Microsoft Office documents remain exposed, especially on Windows and other desktop operating systems.
Google’s approach is to intercept ransomware once it starts encrypting or corrupting files, preventing it from spreading across cloud storage by adding this additional layer of protection to Google Drive.
By the Numbers: The Ransomware Problem
21% – Share of intrusions involving ransomware, according to Mandiant.
$5M+ – Average cost of a ransomware or extortion incident.
25 days – File version retention in Google Drive, enabling file restoration within this window.
0 – Cost to customers; ransomware protection and recovery are included in most Workspace commercial and consumer plans.
Beyond Antivirus: A New Layer of Defense
Traditionally, ransomware protection has been treated as an antivirus problem — scanning for malicious code, blocking it before activation, and quarantining suspicious files. While important, this approach has proven insufficient as ransomware attacks continue to succeed across industries.
Google positions ransomware as more than just an IT issue, noting its ability to disrupt manufacturing lines, retail operations, and hospital services. To address this, Google Drive for desktop adds an entirely new line of defense.
Instead of only stopping ransomware from getting in, Google’s AI-powered detection is designed to stop it from being effective once inside. By detecting attempts to rapidly encrypt or corrupt large groups of files, Google Drive for desktop can immediately pause syncing and isolate the affected content. This creates a protective bubble around a user’s files, stopping ransomware from spreading through the cloud and preventing it from locking important documents and making them unusable.
How It Works: Detect, Pause, Restore
The ransomware protection system in Google Drive for desktop operates in three key steps:
Detection – A specialized AI model, trained on millions of real-world ransomware samples, continuously monitors for unusual file activity, such as rapid attempts to encrypt or corrupt large numbers of files. It adapts to new threats by incorporating updated intelligence from VirusTotal and ongoing analysis of file changes.
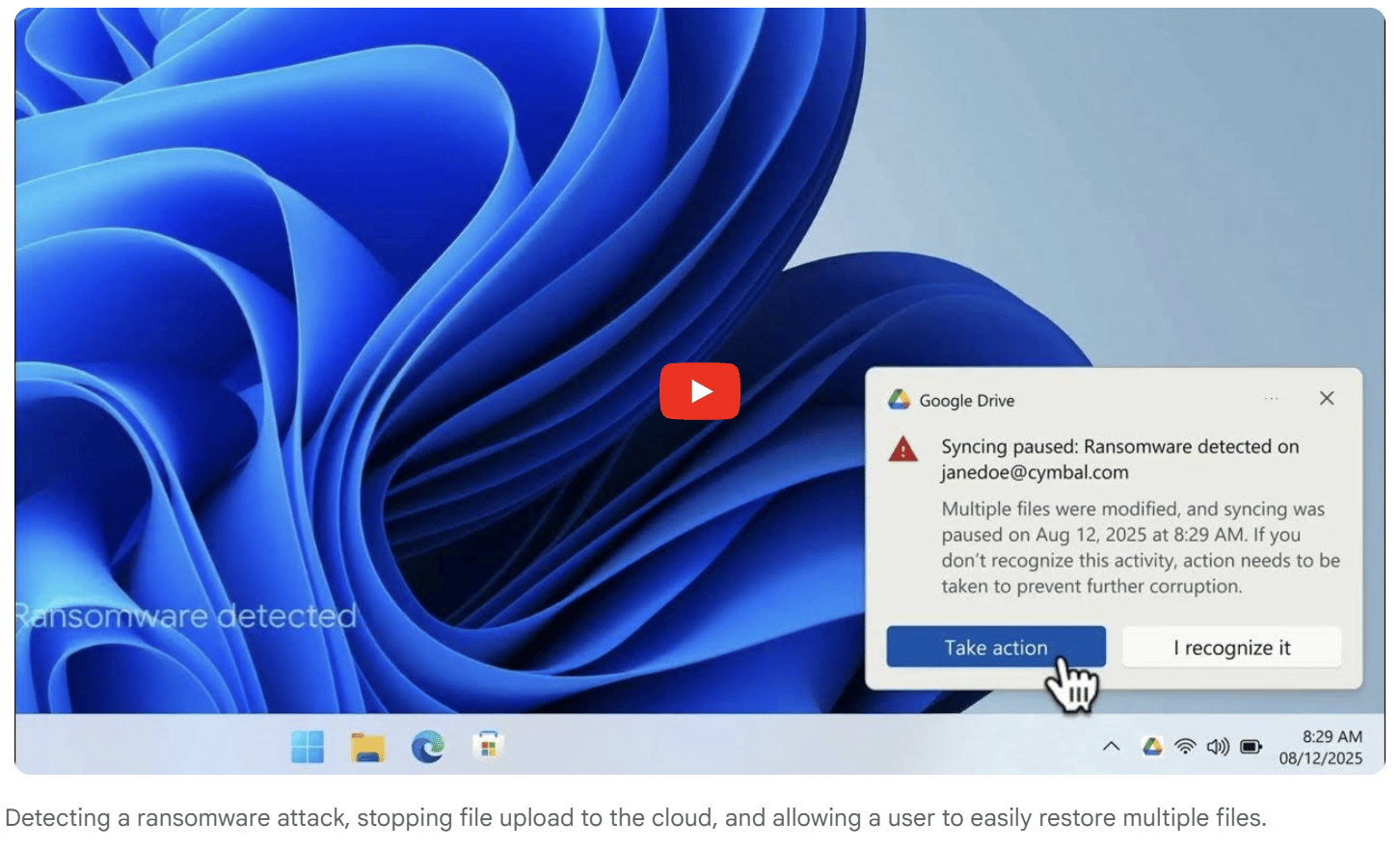
Intervention – When suspicious activity is detected, Drive automatically pauses file syncing to the cloud. This containment step prevents ransomware from spreading further, shields unaffected files from being corrupted, and helps avoid major disruptions to work.
Restoration – Users receive alerts on both desktop and email with clear guidance on how to respond. Through the intuitive Drive web interface, they can restore multiple files at once to a previous, healthy state with just a few clicks. This avoids the need for complex IT re-imaging or expensive third-party recovery tools.
This process helps minimize downtime and data loss, enabling both individual users and organizations to return to normal operations quickly — even when working with traditional software such as Microsoft Windows and Office.
In addition, the built-in virus detection in Google Drive, along with protections in Gmail and Chrome, helps prevent ransomware from spreading to other devices or attempting to take over an entire network. Learn more about these new capabilities and download Google Drive for desktop today.
Admin Visibility and Enterprise Controls
For organizations, administrators gain visibility and control through the Google Workspace Admin Console. Alerts appear in the Security Center when ransomware activity is detected, with access to detailed audit logs.
The feature is enabled by default, though admins can disable end-user recovery if necessary. Google emphasized that no customer data, including AI prompts or generated content, is used for advertising or AI training without explicit permission.
Q&A: Google Drive Ransomware Protection
Q: What is Google announcing?
A: AI-powered ransomware detection and recovery for Google Drive for desktop, rolling out in open beta.
Q: How does it stop ransomware?
A: By detecting suspicious encryption activity, automatically pausing syncing, and allowing users to restore files to a safe state.
Q: Who can use it?
A: Available on Windows and macOS via Google Drive for desktop, included at no extra cost in most Workspace plans.
Q: What about admins?
A: Admins receive alerts and logs in the Admin Console Security Center for oversight and control.
Q: Does Google use my data for AI training?
A: No. Google states that customer data and AI-generated outputs are not used for advertising or model training without explicit permission.
What This Means: AI as a Shield for Cybersecurity
The integration of AI-powered ransomware defense into Google Drive highlights a broader trend: productivity tools are becoming security tools. Instead of relying solely on IT teams or external vendors, everyday cloud services are embedding AI-driven safeguards directly where users work.
For organizations, this lowers the barrier to resilience against one of the most damaging cyber threats. Rapid file recovery reduces downtime, prevents costly disruptions, and limits the need for specialized remediation tools.
For consumers, it adds enterprise-grade protections for free, making secure cloud storage more accessible to individuals and small businesses.
For the AI industry, this launch signals a shift from AI as a productivity booster to AI as a core cybersecurity defense layer. By combining proactive detection with user-friendly recovery, Google is positioning itself as a leader in embedding AI protections at the infrastructure level.
As ransomware continues to grow in scale and sophistication, Google’s move suggests that the future of cybersecurity will increasingly be built into the cloud platforms and productivity tools that people already use daily.
Editor’s Note: This article was created by Alicia Shapiro, CMO of AiNews.com, with writing, image, and idea-generation support from ChatGPT, an AI assistant. However, the final perspective and editorial choices are solely Alicia Shapiro’s. Special thanks to ChatGPT for assistance with research and editorial support in crafting this article.