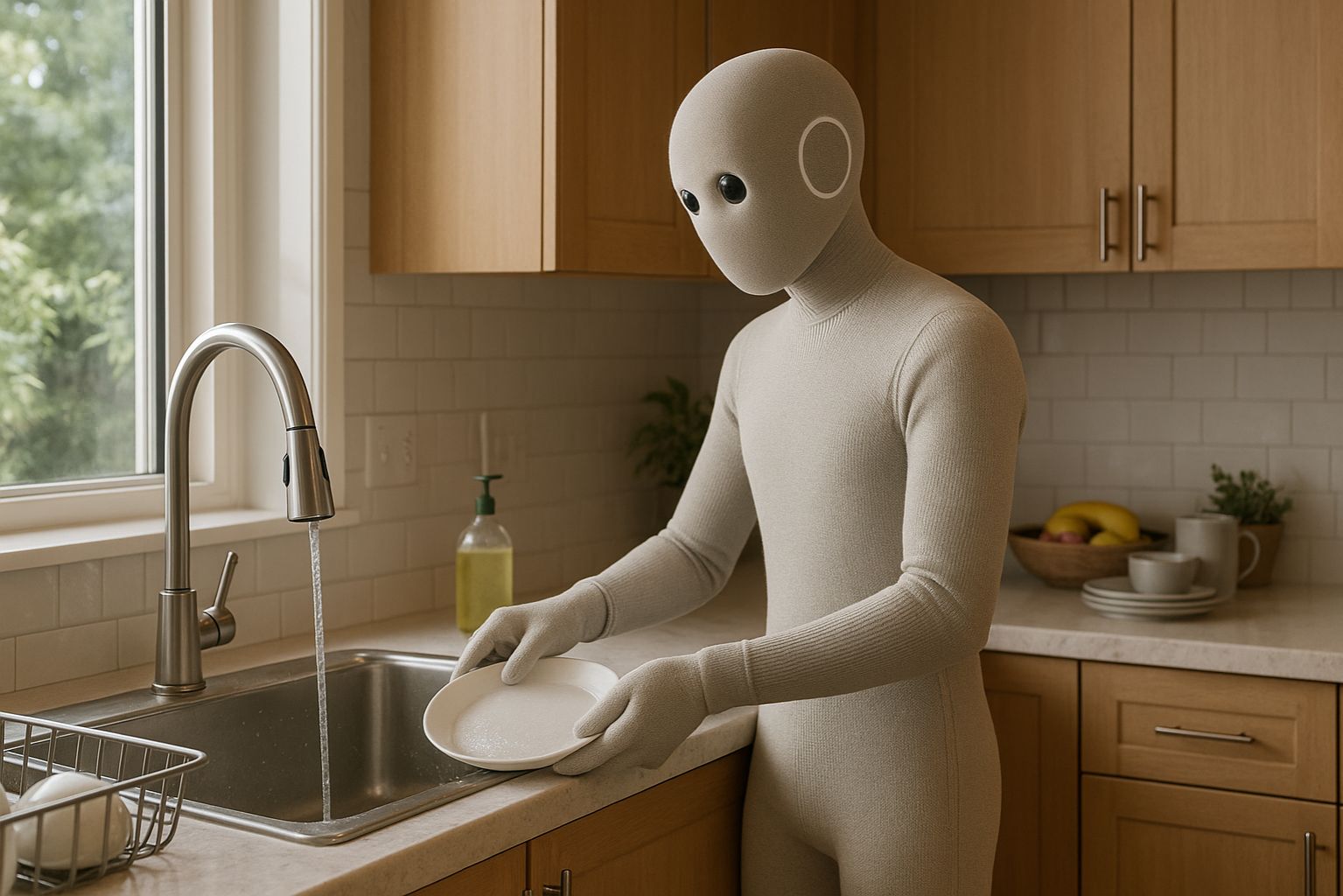
1X’s NEO Home Robot performs household chores like loading the dishwasher, blending futuristic humanoid robotics with everyday convenience for the modern home. Image Source: ChatGPT-5
1X’s NEO Home Robot Launches: $20K or $499/Month for Household Chores
Key Takeaways: NEO Humanoid Robot Launch
1X Technologies opened pre-orders for NEO, offering $20,000 Early Access (ownership) or a $499/month subscription model.
NEO stands about 5'6" tall, weighs 66 lbs, and can lift 154 lbs / carry 55 lbs with a 4-hour battery life and fast charging.
The robot’s soft 3D lattice polymer body and tendon-driven actuators make it safe for homes with people, pets, and furniture.
NEO’s onboard Redwood AI model handles mobility, perception, and learning; its companion 1X World Model “simulates” the outcomes of actions to accelerate real-world learning.
Owners can operate NEO autonomously or schedule a 1X Expert to remotely assist with new tasks.
1X says users can opt out of data sharing, keeping local autonomy without sending personal data to the cloud.
Humanoid Robotics Enter the Home: 1X’s NEO Aims to Redefine Everyday Assistance
If you’ve ever dreamed of having Rosie the Robot from The Jetsons helping around the house, that future may have finally arrived. With the debut of 1X’s NEO Home Robot, everyday chores are about to meet a new kind of intelligence — one that walks, learns, and even tells jokes.
The future of domestic robotics is taking shape as 1X Technologies officially unveils NEO, a humanoid robot designed to perform household chores, assist with daily routines, and adapt to real-world home environments.
Unlike the industrial robots that have long dominated the field, NEO is built specifically for consumers — offering a soft-bodied design, conversational AI, and the ability to fold laundry, carry groceries, or tidy up with gentle precision.
Available through either a $20,000 Early Access purchase or a $499-per-month subscription, NEO represents 1X’s push to make humanoid robotics accessible to everyday households. The company says deliveries will begin in 2026, marking one of the first consumer-ready humanoids intended for the home rather than the factory floor.
Pricing and Availability
1X’s dual-model approach is a strategic bid to make humanoid robotics more attainable. The Early Access program, priced at $20,000, offers full ownership and priority delivery in 2026. Alternatively, the $499/month subscription lets households lease NEO, extending or returning it at the end of the term.
1X confirms that customers who purchase NEO outright for $20,000 will receive standard product support and updates without any additional subscription fees, while subscribers receive full technical support throughout their lease period.
It is not publicly disclosed whether the $499/month subscription path includes a route to ownership (i.e., a lease-to-own conversion), or whether ownership remains only possible via the $20,000 upfront purchase.
Pre-orders require a fully refundable $200 deposit, signaling consumer-market intent rather than a limited research rollout.
Designing for the Home
While humanoid robots have been headline-worthy for years, most have focused on industrial or research applications. NEO is different — it’s explicitly designed for the home. Neo’s marketed theme, “Transform Your Home,” hints at a lifestyle product rather than a lab prototype.
Standing 5 feet 6 inches tall with a soft, deformable polymer body, NEO is meant to blend into human environments. It operates quietly at 22 decibels — quieter than a modern refrigerator — and can fold laundry, carry groceries, organize shelves, or simply chat with its owners.
“The focus is on helping humans in the most diverse environment imaginable — people’s homes,” 1X notes on its website.
Humanlike Motion Through Tendon-Driven Design
What makes NEO’s movements so lifelike is its tendon-driven actuation system, inspired by the way muscles and tendons work in the human body. Instead of relying solely on rigid joints, NEO’s internal architecture uses a network of synthetic tendons and compliant joints to deliver smooth, organic motion.
This allows the robot to bend, crouch, and pick up objects with a natural fluidity uncommon in humanoid robots. The design also improves energy efficiency and safety, since its soft-tissue-like mechanics absorb impact rather than transferring force — a crucial factor for use around people, pets, and delicate household items.
Power Management and Charging
NEO handles its own power management with an internal 0.75 kWh (750 Wh) battery pack, delivering up to four hours of runtime during typical household use and offering a quick-charge mode that restores roughly one hour of operation for about 10 minutes of charging.
When its battery runs low, NEO automatically returns to its dock and plugs itself in, resuming tasks once charged.
According to 1X, NEO is a fully electronic humanoid robot designed for energy efficiency. Based on standard retail electricity rates, the company estimates that operating NEO costs under $1 per day, putting its energy consumption on par with a small household appliance or laptop.
The robot’s adaptive charging system tapers power draw as the battery fills, helping extend battery life while minimizing excess energy use.
The AI Stack Behind NEO
NEO’s intelligence comes from two complementary systems: Redwood AI and the 1X World Model (1XWM).
Redwood AI, a vision-language transformer trained on millions of real-world episodes, runs directly on NEO’s onboard GPU, built on NVIDIA Jetson-class hardware (reportedly the upcoming Thor module). It handles walking, manipulation, and perception in real time — enabling NEO to navigate stairs, sit, kneel, and interact with objects across a home.
The 1X World Model acts like a digital twin — it “hallucinates” potential outcomes of actions before NEO performs them, helping engineers test and improve policies faster without endless real-world trials.
This architecture allows 1X to iterate quickly on autonomy and safety while continuously expanding NEO’s skillset through real-world data collection and simulated reinforcement learning.
Privacy and Tele-Assistance Controls
NEO can perform chores autonomously but also allows owners to schedule sessions with 1X Experts — trained human teleoperators located in the U.S. who can temporarily guide the robot through new or complex tasks.
Importantly, users must grant active consent each time an expert connects. During a remote session, NEO’s ear-ring lights change color to signal that teleoperation is active. 1X emphasizes that experts cannot access NEO without permission, and that owners can end a session at any time.
For privacy-conscious users, the robot operates locally by default and does not store personal data. Any optional data shared with 1X helps improve autonomy but can be opted out of entirely.
Connectivity and Data Use
According to 1X, NEO connects through Wi-Fi and 5G, allowing it to operate autonomously or receive updates without requiring any special setup.
The company notes that only limited sensor data is sent to its servers when fulfilling a specific request, and that this data “isn’t stored.” Users can also opt out of data sharing altogether.
This lightweight approach minimizes bandwidth demands and reinforces 1X’s focus on balancing privacy with performance.
The Competitive Landscape
The humanoid robot space is rapidly evolving, and 1X’s launch of NEO puts it in direct conversation with companies like Figure, Tesla, and Boston Dynamics. While most competitors target industrial or enterprise use, NEO is focused squarely on consumer households.
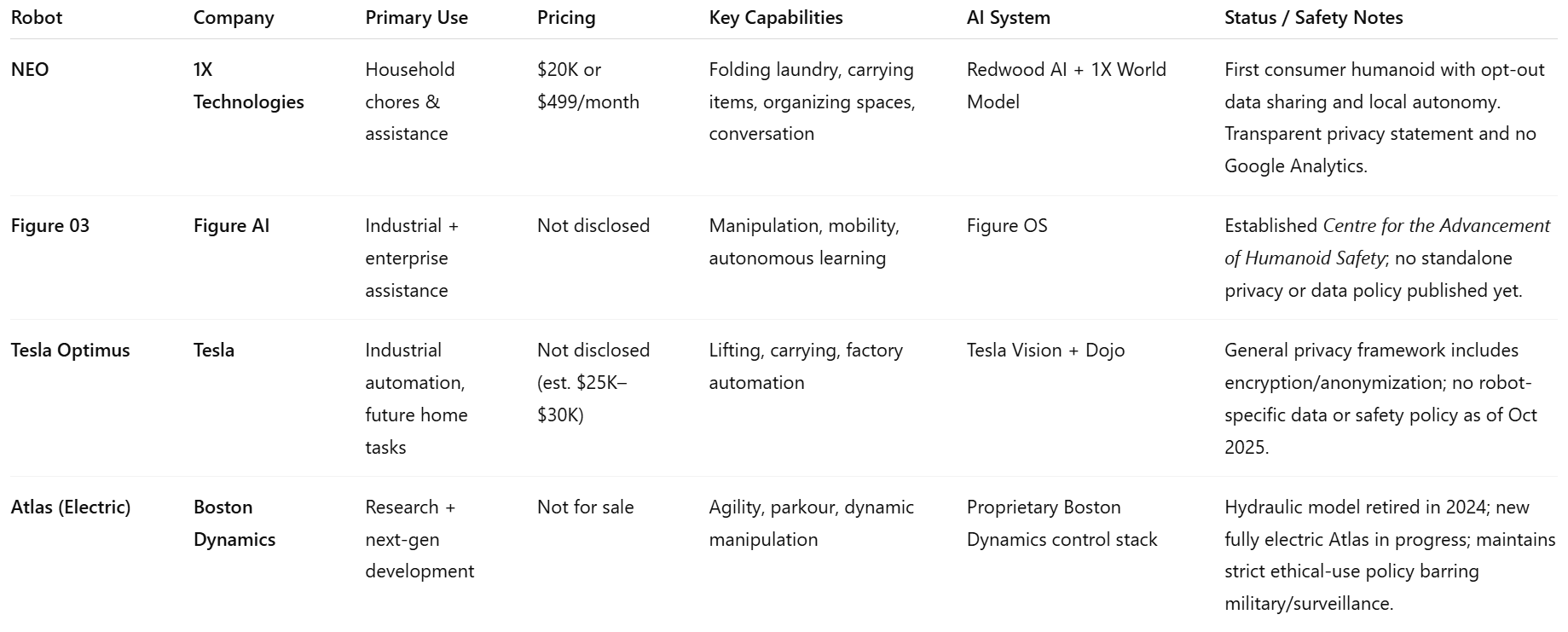
NEO leads the new wave of humanoid robots, distinguishing itself from industrial-focused competitors like Figure 03, Tesla Optimus, and the retired Atlas by targeting household use with transparent pricing and human-centered design. Image Source: ChatGPT-5 created this comparison table.
Safety and Data Ethics in Comparison
Each of these robots reflects a different philosophy around safety, data handling, and trust — a space where 1X appears to be setting a new standard.
1X (NEO)
1X takes the most consumer-friendly stance to date, centering its policy on opt-out data sharing and transparent limits on data use. Its FAQ notes:
“Data collected from real-world tasks refines NEO’s base intelligence and performance, advancing its capabilities and safety. We do not use this data to build a profile of you, nor do we sell this data. If you don’t want to participate in helping improve NEO further, you can always opt out.”
1X’s privacy statement further adds that users can opt out of Google Analytics tracking by using Google’s browser add-on, ensuring more control over how website usage data is collected. This positions NEO as one of the first humanoid robots to prioritize household data ethics as a core feature, not an afterthought.
Figure AI has established the Centre for the Advancement of Humanoid Safety, a dedicated research division focused on workplace injury prevention and mechanical fault compliance aligned with ISO 10218 and ISO/TS 15066 safety standards.
However, as of October 2025, the company has not yet published a standalone privacy or data-handling policy for its humanoid robots.
Tesla (Optimus)
Tesla’s AI division page, where Tesla outlines its mission to build “a general-purpose, bi-pedal, autonomous humanoid robot.” Tesla’s broader corporate privacy framework outlines safeguards such as also, Anonymizati, and opt-in data sharing. However, as of October 2025, the company has not published a dedicated safety or data-handling policy for its humanoid robot, Optimus.
Boston Dynamics (Atlas)
Atlas, originally introduced by Boston Dynamics, had its hydraulic version retired in 2024 and is transitioning toward a fully electric next-generation model.
Boston Dynamics maintains a general privacy policy governing all of its products and an ethical-use framework that prohibits military or surveillance applications — though it has not published a robot-specific privacy statement for Atlas
In this emerging landscape, 1X NEO distinguishes itself as the first humanoid robot to blend enterprise-grade safety engineering with transparent, opt-out consumer data practices — setting a new ethical benchmark for home robotics.
Q&A: NEO’s Capabilities and Limits
Q: Can NEO cook or handle hot appliances?
A: Not yet. NEO’s cooking features are currently disabled for safety. However, it can assist with cleanup and offer recipe guidance through conversational prompts.
Q: How long does NEO run on a charge?
A: Roughly four hours, depending on task complexity. Charging is automatic via a dock that NEO connects to independently.
Q: What makes NEO safe for homes?
A: A tendon-driven actuation system and soft lattice exterior prevent hard impacts, while motion sensors and AI-driven perception systems enable gentle, adaptive movement.
Q: Does it require Wi-Fi?
A: It includes both 5G and Wi-Fi, with most features functional locally even if disconnected.
What This Means: The Human Impact of Home Robotics
The arrival of consumer-ready humanoids like NEO represents a new phase in robotics — one where AI leaves the factory and enters daily life. It’s a signal that the line between utility and companionship is starting to blur.
For many, NEO could become the next household appliance, much like the dishwasher or vacuum once were — only this time, the “appliance” can talk back, adapt, and learn.
While questions remain about long-term affordability and trust, NEO’s launch marks a critical step toward human-centered AI — machines that don’t just automate work but learn to live alongside us.
Editor’s Note: This article was created by Alicia Shapiro, CMO of AiNews.com, with writing, image, and idea-generation support from ChatGPT, an AI assistant used for research and drafting. However, the final perspective and editorial choices are solely Alicia Shapiro’s. Special thanks to ChatGPT for assistance with research and editorial support in crafting this article.

